Table of contents
Understanding of Dementia
Commonness of dementia
Pervasiveness of dementia around the world
Sorts of dementia illness
The 4 typical Sorts of dementia
Dementia side effects
Explicit dementia types have particular side effect profiles
Dementia causes
Dementia causes
Difference between delirium and dementia
Dementia prevention
A dementia conclusion includes an exhaustive assessment
Understanding of Dementia
Dementia progressively decreases mental capability and affects day-to-day routine. Normal side effects include cognitive decline, disarray, bewilderment, and mindset and character changes. It’s brought about by unusual protein gathering in the mind, harming and at last killing nerve cells, prompting cerebrum shrinkage. While there’s no fix, medicines are accessible to manage side effects and work on personal satisfaction. Dementia is likewise referred to as Major Neurocognitive Disorder (MND).
Commonness of dementia
Dementia commonness is supposed to increase with time because of the expansion in the number of individuals aged 65 years or older. The extent of the older population is quicker than that of those under the age of 65
Pervasiveness of dementia around the world
As of now, around the world, more than 60% of individuals live in low- and middle-income nations, and more than 5.5 crore individuals have dementia, and the number is expected to increase by 2050 to 13.1 crore. Almost 1 crore new cases are listed consistently.
Sorts of dementia illness
In light of the causes, dementia is characterized by the accompanying types. Among them, Alzheimer’s is the most widely recognized kind of dementia, yet there are also other types, for example,
Neurodegenerative dementia, Alzheimer’s illness
Lewy body dementia
Blended dementia
Vascular dementia
Frontotemporal dementia
Possibly reversible disorders
Misery
Prescription prompted
Metabolic insanity (Vitamin B12 inadequacy, thyroid problems, thiamine lack, persistent illness, and so on.)
Gastrointestinal problems (Whipple’s disease, vitamin E deficiency, pellagra)
Primary mind sores (Cancer, subdural hematoma, typical tension hydrocephalus)
Overwhelming (Neurosyphilis, HIV/Makes a difference)
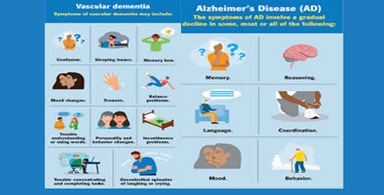
The 4 typical sorts of dementia
Alzheimer’s disorder, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia are depicted under the close-by various kinds of dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most well-known cause of dementia (60-80%), portrayed by beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebrum, prompting neuronal harm and diminished acetylcholine production. Hereditary qualities play a critical part.
Lewy body dementia: Lewy body dementia (5-15%) is brought about by alpha-synuclein protein stores (Lewy bodies) in neurons.
Blended dementia: Blended dementia displays side effects of both Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia.
Vascular dementia: Vascular dementia (20%) results from diminished blood supply to the cerebrum, frequently because of stroke.
Frontotemporal dementia: Frontotemporal dementia influences the front-facing and transient curves, happening at a more youthful age. At last, a few dementias are possibly reversible, frequently brought about by medications, melancholy, or metabolic problems.

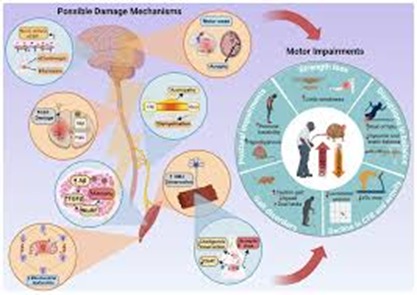
Dementia side effects with a wide range of side effects, including psychosis (fantasies, hallucinations, disturbance, lack of concern, and hostility) and mental shortages (correspondence/language hindrances, cognitive decline, apraxia, agnosia, and impaired executive function). These outcomes from harm to the cerebral cortex due to synaptic disappointment, irritation, and metabolic changes
Explicit dementia types have particular side effect profiles:
Alzheimer’s: Fundamentally momentary cognitive decline at first, advancing to various mental shortfalls (confusion, aphasia, agnosia, apraxia, hindered visuospatial/leader capability) and non-mental side effects (despondency, psychosis, conduct issues). Late-stage side effects include loss of engine control.
Vascular Dementia: Side effects shift given impacted mind areas and stroke severity. Normal issues include disarray, vision loss, bewilderment, discourse difficulties, and unexpected changes in thinking. Cognitive decline may not be available all the time.
Lewy Body Dementia: Portrayed by fluctuating mental impairment, visual fantasies, and Parkinsonism
(Bradykinesia, unbending nature). REM sleep problems are likewise normal. Frontotemporal Dementia: Basically gives character changes and social unsettling influences right off the bat. Visuospatial capability is commonly safeguarded. Dementia risk factors are ordered as modifiable and non-modifiable.
Modifiable gamble factors incorporate less than stellar eating routines, diabetes, hypertension, low instruction levels, weight, horrendous mind injury, hearing misfortune, smoking, unnecessary liquor consumption, absence of active work, elevated cholesterol, high homocysteine levels, and different circumstances like multiple sclerosis, coronary illness, misery, atrial fibrillation, social segregation, air contamination, sleep apnea, and cerebrum diseases.
Non-modifiable risk factors are maturing (the greatest risk factor) and family ancestry/hereditary qualities (including APOE ε4 quality and Down syndrome).
Dementia causes

Dementia is brought about by harm or changes in the cerebrum, frequently because of unusual protein aggregations, prompting nerve cell damage, death, and brain shrinkage.
Normal causes
Normal causes include Alzheimer’s disease, stroke (vascular dementia), Lewy body dementia, Parkinson’s disease, frontotemporal dementia (like Pick’s disease), and extreme head injury.
Uncommon causes
More uncommon causes are leukoencephalopathies, Huntington’s disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, different framework decay, ALS, multiple sclerosis, and diseases (e.g., late-stage syphilis).
Treatable causes
Treatable causes incorporate drug incidental effects, heavy alcohol use, head injury, dizziness, thyroid/kidney/liver issues, brain issues (clusters, growths, diseases), local issues, nutrient lacks, and normal tension hydrocephalus.
Complications of dementia
Dementia complexities can be social/mental and influence different substantial frameworks. These incorporate cognitive decline, pneumonia (normal in frontotemporal dementia), cracks, mental trips, daydreams, disturbance, dysphagia, failure to perform taking care of oneself, unresponsiveness, sadness, bewilderment, a sleeping disorder, issues with critical thinking, misguided thinking, and lack of nutrition.
Difference between delirium and dementia
A key differentiation is between ridiculousness and dementia.
Ridiculousness is a sudden change in cognizance with disarray, creating for hours or days, essentially influencing attention and mindfulness.
Dementia is a progressive mental degradation obstructing free thinking, primarily influencing memory and other cognitive capabilities.
To put it plainly, wooziness is intense and fluctuating, while dementia is constant and moderate.
While there’s no dependable method for forestalling dementia, a healthy way of life can fundamentally decrease the risk. Key protection measures include:
keeping a sound weight, controlling pulse and glucose, remaining genuinely and intellectually dynamic, treating hearing loss, restricting liquor utilization, getting legitimate rest, staying away from tobacco use, and forestalling head wounds.
A dementia conclusion includes an exhaustive assessment:
Clinical history: Social affairs data about the patient’s well-being and side effects.
Mental and neurological tests: Surveying mental capability and neurological well-being.
Lab investigations: Blood tests and lumbar puncture to check for specific markers.
Imaging Tests: CT, X-ray, SPECT, and PET outputs of the mind.
Mental evaluation: Surveying emotional well-being.
Hereditary Tests: Recognizing Hereditary Risk Factors.
Vascular tests: MRA or CTA to analyze the veins in the head and neck.
Mind tests: EEG to gauge cerebrum action.
Heart tests: ECG, echocardiography, and mobile cardiovascular monitoring. There is no remedy for dementia, yet treatment centers around further developing capabilities and personal satisfaction.
Approaches include:
Way of life modifications: Legitimate rest, sufficient activity, a calming diet, and stress decrease.
Non-pharmacological management: Mental preparation, fragrant healing, music treatment, rubbing, conducting strategies, and socialization.
Clinical management: Prescriptions like acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, particularly serotonin reuptake inhibitors, NMDA bad guys, and antipsychotics. Tending to basic circumstances like lack of nutrients, hypothyroidism, and discouragement is additionally vital.


Leave a Reply