Table of contents
Introduction
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that causes the person to have recurrent seizures, and around 3.4 million Americans and 65 million people worldwide suffer from the disease. While relatively common, epilepsy is an enigma with many unanswered questions about its cause, diagnosis, and treatment. In this article, let us cover everything about epilepsy, starting from the facts to the testing to the treatment and therapies.
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a brain disorder involving improper signaling between nerve cells, leading to seizures. Seizures are uncontrolled spikes of electrical activity that affect sensations, behaviors, consciousness, and motor function. Different people have different types of epilepsy, which can lead to different types and frequencies of seizures.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of epilepsy is repeated fits (seizures), which can present themselves in different ways:
Until they were shallow or deep, short or long, asleep or awake.
Loss of control of muscle movement, becoming stiff, or jerking
Loss of sensibility, mood, or behavior changes
Change in hearing, vision, taste, or smell
Numbness or tingling
Psychological markers, like fear, anxiety, or intimidation
Causes and Risk Factors
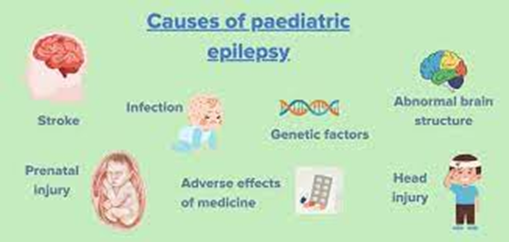
Currently, the cause of epilepsy can be unknown in as many as 70% of all cases, yet contributing factors to its development may include:
Genetics: The inheritance of some varieties of epilepsy from parent to child
Head trauma: A traumatic brain injury may increase the risk of developing epilepsy
Brain infections: Meningitis, encephalitis, or neurocysticercosis can trigger epilepsy
Developmental disorders: Brain formation defects present from birth can increase your risk for epilepsy
Metabolic disorders: Some metabolic disorders can lead to epilepsy
Diagnosis and Tests
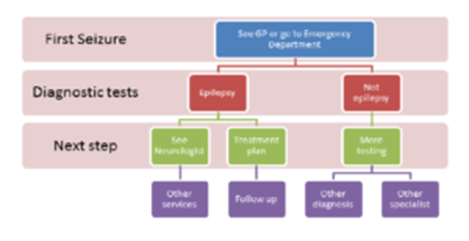
A complete evaluation of a person for epilepsy consists of:
History and physical examination
Electroencephalogram (EEG), for monitoring currents in the brain
Neuroimaging (e.g., MRI/CT) to rule out structural lesions
Additional blood work to exclude other conditions
Treatment Options
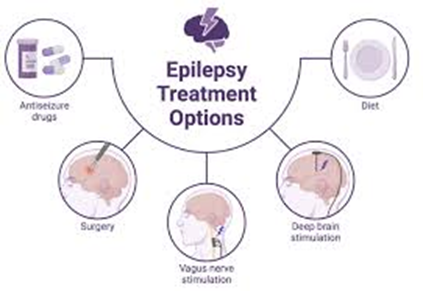
There is no cure for epilepsy, but there are many ways that you can treat seizures, including:
Anti-seizure medications: More than 20 medications may help control seizures. They are then divided up into conductive kinds, and the types of seizure will dictate which drugs, their strength, how long the attack will be, and patient-specific issues.
Diet therapy: Certain diets, such as the ketogenic diet, can help reduce seizures. The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, low-carb diet.
Surgery: Some patients may need surgical resection or disconnection. Surgery is typically offered after patients have failed to have sufficient control of their seizures with medications.
Neuromodulation devices: These implanted devices use a vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) system or responsive neurostimulation (RNS) to detect an oncoming seizure and send electrical impulses to the brain to mitigate the severity.
Therapies
Alongside treatment options, people with epilepsy can explore various types of therapies to help manage their seizure disorder and quality of life:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): A person with epilepsy may benefit from CBT to help him/her manage stress, anxiety, and depression.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy plays an important role in improving movement, balance, and coordination.
Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists can help people with epilepsy gain independence and improve daily living skills.
Nothing feels good, but for those with epilepsy, speech therapy often focuses on beyond-the-limit functional communication.
Support groups: Leverage a support group for emotional support, education, and a sense of community among people facing similar challenges.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies:
A few alternative and complementary treatments can help, especially for people with epilepsy:
Acupuncture: The use of acupuncture has shown limited efficacy in decreasing the frequency of seizures and is used in conjunction with other therapies to promote well-being.
Yoga:

All the benefits yoga can offer you include stress reduction.
Flexibility and overall sense of health improvement.
Mindfulness Meditation:
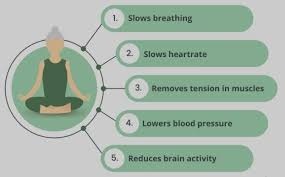
Mindfulness meditation has been shown to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
Supplements: Some herbal products (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids and melatonin)
Possible anti-seizure activity. Activity. Factor.
Conclusion
Epilepsy is a complex and multifactorial disease needing an extensive understanding for long-term treatment and management. There is no cure for epilepsy, but there are treatments and therapies available that can help people with epilepsy control their disease and lead healthy lives. Equipped with a deeper understanding of the condition, treatment options, and therapies, this should give sufferers of epilepsy the confidence they need to address the condition head-on and live their best life.

Leave a Reply